Introduction to Iterative Agile Methodology
Particularly within large organizations, the iterative agile methodology has emerged as a pivotal approach to navigating the complexities of modern project demands. This section aims to elucidate what iterative agile methodology entails, its foundational principles, and its significance in managing large-scale projects effectively.
Definition of Iterative Agile Methodology
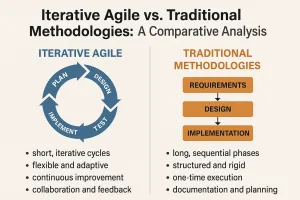
Iterative agile methodology is a framework that emphasizes incremental development and continuous feedback throughout the project lifecycle. Unlike traditional project management approaches that often follow a linear path, iterative agile allows teams to work in short cycles or “sprints,” enabling them to adapt to changes and refine their outputs based on stakeholder feedback. This methodology fosters a collaborative environment where teams can quickly pivot in response to evolving project requirements, ensuring that the final product aligns closely with user needs and expectations.
Overview of Principles and Values of Agile as per the Agile Manifesto
The Agile Manifesto, established in 2001 by a group of software developers, outlines four core values and twelve guiding principles that form the foundation of agile methodologies:
- Core Values:
- Individuals and Interactions over processes and tools: Emphasizing the importance of team collaboration and communication.
- Working Software over comprehensive documentation: Prioritizing functional deliverables that provide value to users.
- Customer Collaboration over contract negotiation: Fostering ongoing engagement with stakeholders to ensure alignment with their needs.
- Responding to Change over following a plan: Encouraging flexibility and adaptability in the face of changing project dynamics.
- Guiding Principles:
- Delivering valuable software early and continuously.
- Welcoming changing requirements, even late in development.
- Maintaining a sustainable pace of work for teams.
- Fostering face-to-face communication as the most effective method of conveying information.
These principles and values collectively promote a culture of responsiveness, collaboration, and continuous improvement, which are essential for the success of large projects.
Importance of Agility in Project Management for Large Organizations
In large organizations, the complexity of projects often increases due to factors such as diverse stakeholder interests, regulatory requirements, and the need for cross-functional collaboration. The iterative agile methodology addresses these challenges by:
- Enhancing Flexibility: Agile allows teams to adapt to changes in project scope or market conditions without derailing the entire project. This flexibility is crucial in large projects where requirements may evolve over time.
- Improving Stakeholder Engagement: Regular feedback loops ensure that stakeholders remain involved throughout the project, leading to higher satisfaction and better alignment with business objectives.
- Facilitating Risk Management: By breaking projects into smaller, manageable increments, teams can identify and mitigate risks early in the development process, reducing the likelihood of significant issues arising later.
- Promoting Continuous Improvement: The iterative nature of agile encourages teams to reflect on their processes and outcomes regularly, fostering a culture of learning and adaptation that is vital for long-term success.
The iterative agile methodology provides a robust framework for managing large projects, enabling organizations to navigate complexities with greater ease and responsiveness. By embracing the principles of agility, project managers can enhance collaboration, improve stakeholder satisfaction, and ultimately deliver higher-quality outcomes.
Understanding the Challenges of Scaling Agile
Scaling agile methodologies in large projects presents a unique set of challenges that project managers must navigate to ensure successful implementation. Here are some key points to consider:
- Complexity of Coordinating Multiple Teams and Stakeholders: In large organizations, agile practices often involve numerous teams working on different components of a project. Coordinating these teams can be complex, as each may have its own priorities, timelines, and workflows. Effective communication and collaboration become critical to avoid silos and ensure that all teams are aligned towards common goals. This complexity can lead to delays and misalignment if not managed properly.
- Maintaining a Unified Vision Across Large, Diverse Teams: With multiple teams involved, maintaining a cohesive vision can be challenging. Each team may interpret the project goals differently, leading to inconsistencies in deliverables and outcomes. Project managers must establish clear objectives and ensure that all teams understand and commit to the overarching vision. Regular alignment meetings and shared documentation can help reinforce this unified direction.
- Balancing Flexibility with the Need for Structure and Governance: Agile methodologies emphasize flexibility and adaptability, which can sometimes clash with the structured governance required in large organizations. Project managers must find a balance between allowing teams the freedom to innovate and ensuring that there are sufficient controls in place to meet compliance and quality standards. This often requires the development of tailored frameworks that incorporate agile principles while still adhering to organizational policies.
- Cultural Resistance to Change Within Established Organizations: Implementing agile at scale often encounters resistance from employees accustomed to traditional project management approaches. This cultural inertia can hinder the adoption of agile practices and create friction among teams. Project managers need to foster a culture of openness and continuous improvement, providing training and support to help teams transition to agile methodologies. Engaging leadership and demonstrating the benefits of agile can also help mitigate resistance.
By addressing these challenges head-on, project managers can better navigate the complexities of scaling agile methodologies in large projects, ultimately leading to more successful outcomes and enhanced collaboration across teams.
Common Pitfalls in Large Agile Implementations
Scaling agile methodologies in large organizations can be a daunting task, often fraught with challenges that can undermine the very principles of agility. Here are some common pitfalls that project managers should be aware of when attempting to implement agile at scale:
- Misunderstanding Agile Principles Leading to ‘Fake’ Agility: One of the most significant challenges is the superficial adoption of agile practices without a true understanding of its core principles. Organizations may implement agile frameworks like Scrum or Kanban but fail to embrace the underlying values of collaboration, flexibility, and customer focus. This can result in a façade of agility, where teams go through the motions without achieving the intended benefits, leading to frustration and disengagement among team members.
- Neglecting Proper Training and Support for Teams: Agile methodologies require a shift in mindset and practices, which necessitates comprehensive training and ongoing support for teams. Organizations often underestimate the importance of equipping their teams with the necessary skills and knowledge to operate effectively within an agile framework. Without proper training, teams may struggle to adapt, leading to inconsistent practices and a lack of alignment across the organization.
- Inadequate Communication Strategies Across Teams: Effective communication is crucial in agile environments, especially when scaling across multiple teams. A common pitfall is the failure to establish robust communication channels that facilitate collaboration and information sharing. When teams operate in silos, it can lead to misunderstandings, duplicated efforts, and a lack of cohesion in project goals. Implementing regular cross-team meetings and utilizing collaborative tools can help mitigate these issues.
- Overemphasis on Tools Rather Than People and Processes: While tools can enhance agile practices, an overreliance on them can detract from the fundamental focus on individuals and interactions. Organizations may invest heavily in software solutions to manage agile processes, but if they neglect the human aspect—such as fostering a culture of trust and collaboration—they risk losing the essence of agility. It is essential to strike a balance between utilizing tools and nurturing the team dynamics that drive successful agile implementations.
By recognizing and addressing these common pitfalls, project managers can better navigate the complexities of scaling agile methodologies in large projects, ultimately leading to more effective and sustainable agile practices within their organizations.
Strategies for Successfully Scaling Agile
Scaling agile methodologies in large projects presents unique challenges that require thoughtful strategies and frameworks. Here are some actionable approaches that project managers can implement to effectively adopt agile practices at scale:
1. Adopting Scaled Frameworks
- SAFe (Scaled Agile Framework): This framework provides a structured approach to scaling agile across large organizations. It emphasizes alignment, collaboration, and delivery across multiple teams. By implementing SAFe, organizations can synchronize their efforts and ensure that all teams are working towards common goals.
- LeSS (Large Scale Scrum): LeSS extends Scrum principles to large-scale projects, maintaining simplicity while addressing the complexities of multiple teams working together. It focuses on transparency and empiricism, allowing teams to adapt and improve continuously.
2. Establishing Clear Roles and Responsibilities
- Clearly defined roles are crucial for enhancing accountability within teams. In a scaled agile environment, it is essential to delineate responsibilities among team members, product owners, and stakeholders. This clarity helps prevent overlaps and confusion, ensuring that everyone understands their contributions to the project.
- Consider implementing role-specific training to equip team members with the necessary skills and knowledge to fulfill their responsibilities effectively.
3. Fostering a Culture of Collaboration and Continuous Improvement
- Cultivating a collaborative culture is vital for the success of agile at scale. Encourage open communication and teamwork across all levels of the organization. This can be achieved through regular cross-team meetings, workshops, and team-building activities that promote trust and cooperation.
- Emphasize the importance of continuous improvement by implementing regular retrospectives at both team and program levels. This practice allows teams to reflect on their processes, identify areas for improvement, and adapt their practices accordingly.
4. Investing in Robust Communication Tools and Practices
- Effective communication is the backbone of successful agile implementation. Invest in tools that facilitate real-time collaboration, such as project management software, instant messaging platforms, and video conferencing tools. These resources help bridge the gap between distributed teams and ensure that everyone stays informed and engaged.
- Establish communication protocols that outline how information is shared across teams. This includes regular updates, status reports, and feedback loops that keep all stakeholders aligned and informed about project progress.
By implementing these strategies, project managers can navigate the complexities of scaling agile methodologies in large organizations. The key lies in fostering an environment that supports collaboration, accountability, and continuous improvement, ultimately leading to more successful project outcomes.
Monitoring and Adapting Agile Practices
Particularly within large organizations, the application of iterative agile methodologies presents unique challenges. As teams scale, the need for continuous monitoring and adaptation becomes paramount to ensure that agile practices remain effective and aligned with project goals. Here are some key points to consider:
- Utilizing Metrics and KPIs to Assess Agile Effectiveness: Establishing clear metrics and Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) is essential for evaluating the success of agile practices. Metrics such as velocity, cycle time, and lead time can provide insights into team performance and project progress. By regularly reviewing these metrics, project managers can identify areas for improvement and make informed decisions to enhance productivity and efficiency.
- Encouraging Feedback Loops and Retrospectives Among Teams: Feedback is a cornerstone of agile methodologies. Implementing regular retrospectives allows teams to reflect on their processes, celebrate successes, and identify challenges. This practice fosters a culture of open communication and continuous improvement, enabling teams to adapt their strategies based on real-time insights and experiences. Encouraging cross-team feedback can also enhance collaboration and knowledge sharing across the organization.
- Adjusting Processes Based on Team Dynamics and Project Needs: Agile is not a one-size-fits-all approach; it requires flexibility to adapt to the unique dynamics of each team and the specific needs of the project. Project managers should be prepared to modify workflows, roles, and responsibilities as necessary. This adaptability ensures that teams can respond effectively to changing requirements and maintain momentum throughout the project lifecycle.
- Creating a Flexible Environment that Embraces Change: A successful agile implementation in large projects hinges on fostering an organizational culture that embraces change. This involves not only supporting teams in their agile practices but also encouraging a mindset that views change as an opportunity for growth. By cultivating an environment where experimentation is welcomed and failures are seen as learning experiences, organizations can enhance their agility and responsiveness to market demands.
Monitoring and adapting agile practices is crucial for overcoming the complexities of scaling agile methodologies in large projects. By leveraging metrics, fostering feedback, adjusting processes, and creating a flexible environment, project managers can navigate the challenges of agile at scale and drive successful project outcomes.
Conclusion: The Future of Agile in Large Organizations
As organizations continue to navigate the complexities of large-scale projects, the iterative agile methodology has emerged as a powerful framework that can drive efficiency, collaboration, and innovation. Despite the inherent challenges of scaling agile practices, the benefits are significant and can lead to transformative outcomes for project management in large organizations.
Recap of the Benefits of Scaling Agile
- Enhanced Flexibility and Responsiveness: Scaling agile allows teams to respond more swiftly to changes in project requirements and market conditions. This adaptability is crucial in today’s fast-paced business environment, where customer needs can shift rapidly.
- Improved Collaboration and Communication: Agile methodologies promote a culture of collaboration, breaking down silos between departments. This fosters better communication and teamwork, which are essential for the success of large projects.
- Increased Customer Satisfaction: By involving stakeholders throughout the project lifecycle and delivering incremental value, organizations can ensure that the final product aligns closely with customer expectations, leading to higher satisfaction rates.
- Higher Quality Deliverables: The iterative nature of agile allows for continuous testing and feedback, which helps in identifying and addressing issues early in the development process, ultimately resulting in higher quality outcomes.
Embracing Agility as a Mindset
For project managers in large organizations, embracing agility is not just about implementing a set of practices; it is about adopting a mindset that values flexibility, collaboration, and continuous improvement. This cultural shift is essential for overcoming the challenges associated with scaling agile methodologies. By fostering an environment that encourages experimentation and learning from failures, organizations can better position themselves to thrive.
It is imperative for project managers to commit to continuous learning and adaptation. This involves:
- Investing in Training and Development: Organizations should prioritize training programs that equip teams with the skills and knowledge necessary to implement agile practices effectively.
- Encouraging Knowledge Sharing: Creating platforms for sharing experiences and best practices can help teams learn from one another and refine their agile approaches.
- Staying Informed on Industry Trends: Project managers should actively seek out new methodologies, tools, and frameworks that can enhance their agile practices and address the unique challenges of large projects.
While scaling agile methodologies in large organizations presents its own set of challenges, the potential benefits far outweigh the difficulties. By embracing agility as a core mindset and committing to ongoing learning and adaptation, project managers can lead their teams to success in an increasingly complex project environment. The future of agile in large organizations is bright, and those who are willing to evolve will undoubtedly reap the rewards.
Find out more about Shaun Stoltz https://www.shaunstoltz.com/about/.
This post was written by an AI and reviewed/edited by a human.