Introduction to Agile Gantt Charts
The tools and methodologies employed can significantly influence both the success of projects and the professional growth of project managers. One such tool that has evolved to meet the demands of modern project management is the agile Gantt chart. This section aims to provide a foundational understanding of agile Gantt charts, their definition, their comparison with traditional Gantt charts, and their role within agile project management methodologies.
Definition of Agile Gantt Charts
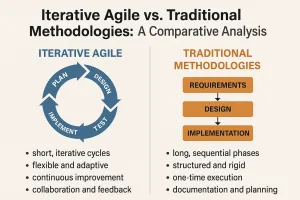
Agile Gantt charts are a visual project management tool that combines the traditional Gantt chart’s timeline and task management features with the flexibility and iterative nature of agile methodologies. Unlike standard Gantt charts, which typically represent a linear progression of tasks and dependencies, agile Gantt charts allow for adjustments and real-time updates, reflecting the dynamic nature of agile projects. They help teams visualize project timelines while accommodating changes in scope, priorities, and resources, making them particularly useful in environments where adaptability is crucial.
Comparison of Traditional Gantt Charts and Agile Gantt Charts
- Structure and Flexibility: Traditional Gantt charts are often rigid, displaying a fixed sequence of tasks and their dependencies. In contrast, agile Gantt charts are designed to be more flexible, allowing project managers to modify timelines and tasks as project requirements evolve. This adaptability is essential in agile environments where change is frequent and expected.
- Focus on Iteration: Traditional Gantt charts typically focus on the completion of tasks in a linear fashion, which can lead to challenges in fast-paced projects. Agile Gantt charts, however, emphasize iterative progress, breaking down projects into smaller, manageable increments or sprints. This approach not only enhances visibility but also fosters continuous improvement and feedback.
- Collaboration and Communication: Agile Gantt charts promote collaboration among team members by providing a shared visual representation of project progress. This contrasts with traditional Gantt charts, which may be used primarily by project managers to track progress. The collaborative nature of agile Gantt charts encourages team engagement and accountability, which can lead to improved job performance and career growth for project managers.
The Role of Gantt Charts in Agile Project Management Methodologies
In agile project management methodologies, Gantt charts serve several critical functions:
- Visualizing Progress: Agile Gantt charts provide a clear visual representation of project timelines, helping teams track progress against their goals. This visibility is essential for identifying bottlenecks and ensuring that projects remain on track.
- Facilitating Planning and Prioritization: By illustrating task dependencies and timelines, agile Gantt charts assist project managers in planning and prioritizing work effectively. This capability is vital in agile environments, where priorities can shift rapidly based on stakeholder feedback and changing market conditions.
- Enhancing Stakeholder Communication: Agile Gantt charts can be an effective communication tool for stakeholders, providing them with a straightforward overview of project status and timelines. This transparency fosters trust and collaboration between project teams and stakeholders, ultimately contributing to project success.
Agile Gantt charts represent a significant advancement in project management tools, offering a blend of structure and flexibility that aligns with the principles of agile methodologies. By understanding their definition, comparing them with traditional Gantt charts, and recognizing their role in agile project management, project managers can leverage these tools to enhance their career growth and job performance.
The Evolution of Project Management Tools
Project management has undergone significant transformations over the decades, driven by the need for more efficient, flexible, and collaborative approaches to managing projects. Understanding this evolution is crucial for project managers and career development professionals, especially as they navigate the integration of agile methodologies and tools like agile Gantt charts into their workflows.
Historical Overview of Project Management Tools
- Early Tools and Techniques: The roots of project management can be traced back to the early 20th century with tools like Gantt charts and the Critical Path Method (CPM). Gantt charts, developed by Henry Gantt in the 1910s, provided a visual representation of project schedules, allowing managers to track progress and allocate resources effectively. These tools were primarily used in construction and manufacturing, where tasks were linear and sequential.
- The Rise of Software Solutions: As technology advanced, project management tools evolved from manual charts to sophisticated software solutions. The 1980s and 1990s saw the introduction of software like Microsoft Project, which automated Gantt charts and allowed for more complex project planning and tracking. This era marked a shift towards more structured project management practices, emphasizing detailed planning and control.
Shift from Traditional to Agile Methodologies
- The Agile Manifesto: In the early 2000s, the Agile Manifesto was introduced, advocating for a more flexible and iterative approach to project management. Agile methodologies prioritize customer collaboration, responsiveness to change, and delivering small, incremental improvements. This shift challenged the traditional project management paradigms that relied heavily on upfront planning and rigid timelines.
- Impact on Project Management Tools: The adoption of agile methodologies necessitated the development of new tools that could accommodate iterative processes and facilitate collaboration among team members. Traditional Gantt charts, which often represented a static view of project timelines, were reimagined to support agile practices. Agile Gantt charts emerged as a hybrid tool, combining the visual scheduling benefits of Gantt charts with the flexibility of agile methodologies.
Emergence and Growth of Hybrid Project Management Approaches
- Blending Agile and Traditional Practices: As organizations recognized the benefits of both agile and traditional project management, hybrid approaches began to gain traction. These methodologies allow teams to leverage the structured planning of traditional tools while embracing the adaptability of agile practices. Agile Gantt charts play a pivotal role in this hybrid model, providing a visual framework that accommodates changing project requirements and timelines.
- Career Implications for Project Managers: Understanding and utilizing agile Gantt charts can significantly influence a project manager’s career growth and job performance. By mastering these tools, project managers can enhance their ability to manage complex projects, improve team collaboration, and respond effectively to stakeholder needs. This adaptability not only positions them as valuable assets within their organizations but also opens up new career opportunities in an increasingly agile-focused job market.
The evolution of project management tools reflects a broader shift towards flexibility and collaboration in managing projects. Agile Gantt charts exemplify this transformation, offering project managers a powerful tool to navigate the complexities of modern project environments while fostering career development and enhancing job performance.
Benefits of Using Agile Gantt Charts
The integration of Agile methodologies with Gantt charts has emerged as a powerful tool that can significantly enhance both project execution and career development for professionals in the field. Here are some key benefits of using Agile Gantt charts:
- Enhanced Visibility and Transparency in Project Progress
Agile Gantt charts provide a clear visual representation of project timelines, tasks, and milestones. This transparency allows project managers and team members to easily track progress and identify potential bottlenecks. By having a comprehensive view of the project status, stakeholders can make informed decisions quickly, which is crucial in fast-paced environments. This visibility not only aids in project execution but also builds trust among team members and stakeholders, fostering a culture of accountability and openness. - Improved Adaptability to Changes and Feedback
One of the core principles of Agile is its responsiveness to change. Agile Gantt charts facilitate this adaptability by allowing project managers to adjust timelines and tasks dynamically as new information or feedback emerges. This flexibility is essential in today’s rapidly changing business environment, where project requirements can shift unexpectedly. By effectively managing changes, project managers can ensure that their teams remain aligned with project goals, ultimately leading to higher job performance and satisfaction. - Facilitation of Collaboration Among Team Members
Agile Gantt charts promote collaboration by providing a shared platform where all team members can view and contribute to the project plan. This collaborative environment encourages communication and teamwork, as team members can easily see how their tasks interconnect with others. Enhanced collaboration not only improves project outcomes but also contributes to individual career growth, as professionals develop their teamwork and communication skills, which are highly valued in the job market.
The use of Agile Gantt charts in project management offers significant advantages that can influence career growth and job performance. By enhancing visibility, improving adaptability, and facilitating collaboration, these tools empower project managers and their teams to navigate complex projects more effectively, ultimately leading to successful project outcomes and professional development.
Impact on Career Growth for Project Managers
Proficiency in agile methodologies, particularly the use of agile Gantt charts, can significantly influence career growth and job performance for project managers. Here are several key points that illustrate this impact:
- Increased Marketability and Job Opportunities: As organizations increasingly adopt agile practices, project managers who are skilled in agile Gantt charts become more marketable. These charts provide a visual representation of project timelines and tasks, allowing for better planning and adaptability. Employers are actively seeking professionals who can navigate both traditional and agile project management frameworks, making those with agile Gantt chart expertise more attractive candidates in a competitive job market.
- Skills in Demand: Agile Methodologies and Tools: The demand for agile skills is on the rise, with many companies prioritizing candidates who can effectively implement agile practices. Agile Gantt charts are a valuable tool that combines the flexibility of agile with the structured approach of Gantt charts, enabling project managers to manage projects more efficiently. Mastery of these tools not only enhances a project manager’s skill set but also positions them as leaders in their field, capable of driving successful project outcomes.
- Case Studies of Career Advancement Due to Agile Expertise: Numerous project managers have experienced significant career advancements by embracing agile methodologies. For instance, a project manager who transitioned from traditional project management to agile practices, including the use of agile Gantt charts, reported a promotion to a senior management position within a year. This advancement was attributed to their ability to lead agile teams effectively and deliver projects that met changing client needs. Such case studies highlight the tangible benefits of agile expertise in career progression.
The integration of agile Gantt charts into project management practices not only enhances project execution but also serves as a catalyst for career growth. By developing proficiency in these tools, project managers can increase their marketability, meet the demands of modern workplaces, and position themselves for advancement in their careers.
Influencing Job Performance with Agile Gantt Charts
Agile Gantt charts are an innovative tool that combines the traditional Gantt chart’s visual timeline with the flexibility of agile project management methodologies. This hybrid approach not only enhances project tracking but also significantly influences job performance and career growth for project managers. Here are some key points to consider:
Examples of Successful Project Completions Using Agile Gantt Charts
- Enhanced Visibility and Collaboration: Agile Gantt charts provide a clear visual representation of project timelines, tasks, and dependencies. For instance, a software development team at a tech startup utilized agile Gantt charts to manage their sprint cycles effectively. By visualizing tasks and progress, they improved team collaboration and completed their project two weeks ahead of schedule, leading to a successful product launch.
- Adaptability to Change: In a case study involving a marketing agency, the use of agile Gantt charts allowed the team to quickly adapt to changing client requirements. By breaking down projects into smaller, manageable tasks and adjusting timelines dynamically, they were able to deliver high-quality campaigns that exceeded client expectations, resulting in a 30% increase in client retention rates.
Metrics for Measuring Performance Improvements
To assess the impact of agile Gantt charts on job performance, project managers can utilize several key performance indicators (KPIs):
- On-Time Delivery Rate: Tracking the percentage of tasks completed on or before their deadlines can provide insights into how agile Gantt charts facilitate timely project completions. Teams that adopted this tool reported a 25% improvement in on-time delivery rates.
- Team Productivity: Measuring the output of team members before and after implementing agile Gantt charts can highlight productivity gains. For example, a project team noted a 40% increase in task completion rates, attributed to better task prioritization and clearer timelines.
- Stakeholder Satisfaction: Gathering feedback from stakeholders regarding project outcomes can help gauge the effectiveness of agile Gantt charts. A project manager from a construction firm shared that stakeholder satisfaction scores improved by 15% after they began using agile Gantt charts, as clients appreciated the transparency and regular updates.
Real-Life Testimonials from Project Managers
- Testimonial 1: “Implementing agile Gantt charts transformed our project management approach. We were able to visualize our progress and adapt quickly to changes, which ultimately led to a successful product launch ahead of schedule.” – Sarah, Project Manager at a Tech Startup.
- Testimonial 2: “The flexibility of agile Gantt charts allowed my team to manage multiple projects simultaneously without losing sight of deadlines. Our productivity soared, and our clients noticed the difference.” – John, Senior Project Manager at a Marketing Agency.
- Testimonial 3: “Using agile Gantt charts has not only improved our project outcomes but also enhanced team morale. Everyone is more engaged when they can see how their work contributes to the bigger picture.” – Emily, Project Manager at a Construction Firm.
Agile Gantt charts are more than just a project management tool; they are a catalyst for improved job performance and career advancement. By facilitating better visibility, adaptability, and collaboration, these charts empower project managers to deliver successful projects consistently. As the demand for agile methodologies continues to grow, mastering agile Gantt charts can significantly enhance a project manager’s skill set and career trajectory.
Challenges and Limitations of Agile Gantt Charts
Agile Gantt charts have emerged as a valuable tool in project management, blending traditional Gantt chart features with agile methodologies. However, their implementation is not without challenges and limitations. Understanding these drawbacks is crucial for project managers and career development professionals aiming to leverage agile Gantt charts effectively. Here are some key points to consider:
Common Misconceptions about Agile Gantt Charts
- Static vs. Dynamic Nature: One prevalent misconception is that Gantt charts are inherently static and do not align with the agile principle of adaptability. While traditional Gantt charts often depict fixed timelines, agile Gantt charts can be designed to reflect iterative progress and accommodate changes in project scope or priorities. This flexibility is essential for teams that operate in fast-paced environments, yet the misconception can lead to resistance in adopting this tool.
- Misunderstanding Agile Principles: Another misconception is that using Gantt charts contradicts agile principles. In reality, agile methodologies emphasize collaboration and responsiveness, and Gantt charts can enhance these aspects by providing a visual representation of project timelines and dependencies. However, if project managers rely solely on Gantt charts without integrating agile practices, they may undermine the very principles they aim to uphold.
Limitations in Complex Project Scenarios
- Complexity and Overhead: In large-scale or complex projects, agile Gantt charts can become cumbersome. The need to update the chart frequently to reflect changes in tasks, timelines, and team responsibilities can lead to administrative overhead. This complexity may detract from the agile focus on delivering value and responding to change, as teams may spend more time managing the chart than executing tasks.
- Difficulty in Capturing Non-linear Workflows: Agile projects often involve non-linear workflows, where tasks may not follow a sequential order. Traditional Gantt charts are designed for linear task management, which can make it challenging to represent the iterative nature of agile work. This limitation can lead to confusion among team members regarding task priorities and dependencies.
Strategies to Overcome These Challenges
- Emphasize Collaboration: To mitigate the limitations of agile Gantt charts, project managers should emphasize collaboration among team members. Regularly scheduled meetings, such as daily stand-ups or sprint reviews, can help ensure that everyone is aligned on project goals and timelines, reducing the reliance on the Gantt chart as the sole source of truth.
- Utilize Agile Tools: Incorporating agile project management tools that integrate Gantt chart features can streamline the process. Tools like Jira, Trello, or Asana offer functionalities that allow teams to visualize their work while maintaining the flexibility of agile methodologies. These tools can help manage tasks dynamically, reducing the administrative burden associated with traditional Gantt charts.
- Focus on Key Milestones: Instead of attempting to map every task in detail, project managers can focus on key milestones and deliverables within the Gantt chart. This approach allows teams to maintain a high-level overview of the project while still being agile in their execution. By prioritizing essential tasks, teams can adapt more readily to changes without losing sight of overall project goals.
While agile Gantt charts offer a unique blend of structure and flexibility, they come with their own set of challenges and limitations. By addressing common misconceptions, recognizing the limitations in complex scenarios, and implementing effective strategies, project managers can harness the benefits of agile Gantt charts to enhance their career growth and job performance.
Best Practices for Implementing Agile Gantt Charts
Agile Gantt charts are a powerful tool in project management that can enhance visibility, improve communication, and facilitate better planning. For project managers looking to implement these charts effectively, here are some best practices to consider:
Step-by-Step Guide to Creating an Agile Gantt Chart
- Define Project Scope and Objectives:
- Begin by clearly outlining the project goals and deliverables. This will help in identifying the key tasks and milestones that need to be included in the Gantt chart.
- Break Down Tasks:
- Decompose the project into smaller, manageable tasks. Each task should be specific and measurable, allowing for easier tracking and adjustments as the project progresses.
- Establish Timeframes:
- Assign realistic timeframes for each task. In an agile environment, these timeframes may be flexible, but having a baseline helps in planning sprints and iterations.
- Identify Dependencies:
- Determine which tasks are dependent on others. This will help in visualizing the flow of the project and understanding how delays in one area may impact others.
- Use Agile Methodologies:
- Incorporate agile principles by allowing for iterative updates to the Gantt chart. Regularly review and adjust the chart during sprint planning meetings to reflect changes in priorities or timelines.
- Visualize Progress:
- Use color coding or markers to indicate the status of tasks (e.g., completed, in progress, or delayed). This visual representation aids in quick assessments of project health.
Tools and Software Recommendations
- Trello: A flexible tool that allows for the creation of boards and cards, which can be adapted to represent Gantt charts through various plugins.
- Asana: Offers timeline features that can be used to create Gantt-style views, making it easy to track project progress and deadlines.
- Microsoft Project: A more traditional project management tool that provides robust Gantt chart capabilities, suitable for larger projects.
- Smartsheet: Combines the functionality of spreadsheets with Gantt chart features, allowing for easy collaboration and updates.
- Monday.com: A user-friendly platform that supports Gantt charts and integrates well with other agile tools, enhancing team collaboration.
Tips for Integrating Agile Gantt Charts into Existing Workflows
- Train Your Team: Ensure that all team members understand how to use the Gantt chart effectively. Provide training sessions or resources to familiarize them with the tool and its benefits.
- Regular Updates: Schedule regular check-ins to update the Gantt chart. This could be during daily stand-ups or weekly reviews, ensuring that the chart reflects the most current project status.
- Encourage Collaboration: Foster an environment where team members can contribute to the Gantt chart. This collaborative approach can lead to more accurate timelines and a shared understanding of project goals.
- Be Flexible: Embrace the agile philosophy of adaptability. Be prepared to modify the Gantt chart as project requirements change, and encourage your team to provide input on necessary adjustments.
- Leverage Feedback: After implementing the Gantt chart, gather feedback from your team on its effectiveness. Use this input to refine your approach and improve future iterations.
By following these best practices, project managers can effectively implement agile Gantt charts, enhancing their project management capabilities and ultimately contributing to career growth and improved job performance.
Future Trends in Project Management and Agile Gantt Charts
The integration of agile methodologies with traditional tools like Gantt charts is becoming increasingly significant. This section explores the future trends that will shape the role of agile Gantt charts in project management, particularly in relation to emerging technologies, predicted changes in methodologies, and their ongoing relevance in a digital environment.
Emerging Technologies Influencing Project Management Tools
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning: These technologies are set to revolutionize project management by automating routine tasks, providing predictive analytics, and enhancing decision-making processes. Agile Gantt charts can leverage AI to offer real-time updates and insights, allowing project managers to adjust timelines and resources dynamically based on project progress and team performance.
- Cloud Computing: The shift to cloud-based project management tools facilitates collaboration across geographically dispersed teams. Agile Gantt charts hosted in the cloud can be accessed and updated in real-time, ensuring that all team members are aligned and informed, which is crucial for agile project success.
- Collaboration Tools: Platforms like Slack, Microsoft Teams, and Asana are increasingly integrated with project management tools. Agile Gantt charts can be enhanced with features that allow for seamless communication and collaboration, enabling teams to respond quickly to changes and maintain agility.
Predicted Changes in Project Management Methodologies
- Hybrid Methodologies: The future of project management is likely to see a blend of agile and traditional methodologies. Agile Gantt charts will play a pivotal role in this hybrid approach, providing a visual representation of project timelines while accommodating the flexibility required by agile practices. This adaptability will help project managers balance structure with responsiveness.
- Increased Focus on Agile Practices: As organizations continue to embrace agile principles, the demand for tools that support these practices will grow. Agile Gantt charts will evolve to incorporate features that reflect agile workflows, such as sprints, backlogs, and iterative planning, making them more relevant in agile environments.
- Emphasis on Continuous Improvement: Future project management will prioritize continuous improvement and learning. Agile Gantt charts can facilitate this by allowing teams to visualize their progress and identify areas for enhancement, thus fostering a culture of reflection and adaptation.
Ongoing Relevance of Agile Gantt Charts in a Digital
- Visual Management: In a digital age where information overload is common, the visual nature of Gantt charts remains a powerful tool for project managers. Agile Gantt charts can simplify complex project timelines, making it easier for stakeholders to understand project status at a glance.
- Integration with Agile Frameworks: As agile frameworks like Scrum and Kanban gain traction, agile Gantt charts will need to adapt to incorporate elements from these methodologies. This integration will ensure that Gantt charts remain relevant and useful for teams practicing agile project management.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: The future of project management will be heavily influenced by data analytics. Agile Gantt charts can be enhanced with data visualization tools that provide insights into project performance, resource allocation, and risk management, enabling project managers to make informed decisions quickly.
The future of agile Gantt charts in project management is promising, driven by technological advancements and evolving methodologies. As project managers embrace these changes, agile Gantt charts will continue to be a vital tool, influencing career growth and job performance by enhancing project visibility, adaptability, and collaboration.
Conclusion
The integration of agile methodologies with traditional tools like Gantt charts presents a unique opportunity for professionals to enhance their effectiveness and career trajectories. Agile Gantt charts serve as a bridge between the structured planning of traditional project management and the flexibility required in agile environments. Here are the key takeaways regarding their benefits and professional implications:
- Enhanced Visibility and Communication: Agile Gantt charts provide a clear visual representation of project timelines and progress, facilitating better communication among team members and stakeholders. This transparency fosters collaboration and ensures everyone is aligned with project goals, which is crucial for career advancement in project management roles.
- Improved Adaptability: By incorporating agile principles, Gantt charts allow project managers to quickly adjust timelines and resources in response to changing project requirements. This adaptability not only improves project outcomes but also positions project managers as agile leaders, enhancing their professional reputation and career prospects.
- Increased Efficiency: The combination of agile methodologies with Gantt charts streamlines project planning and execution. Project managers can identify bottlenecks and allocate resources more effectively, leading to improved job performance and the successful delivery of projects on time and within budget.
- Skill Development: Embracing agile Gantt charts encourages project managers to develop a diverse skill set that includes both traditional project management techniques and agile practices. This continuous learning is essential for career growth, as it equips professionals with the tools needed to navigate complex project environments.
As project managers, it is vital to remain open to new methodologies and tools that can enhance your effectiveness. Embracing agile Gantt charts is not just about adopting a new tool; it is about fostering a mindset of continuous improvement and adaptability.
Find out more about Shaun Stoltz https://www.shaunstoltz.com/about/.
This post was written by an AI and reviewed/edited by a human.