Introduction to Program Life Cycle
The program life cycle serves as a crucial framework that guides the planning, execution, and completion of programs. Understanding this life cycle is essential for compliance officers and project managers alike, as it not only ensures the successful delivery of projects but also aligns with industry standards and regulations.
Definition of Program Life Cycle
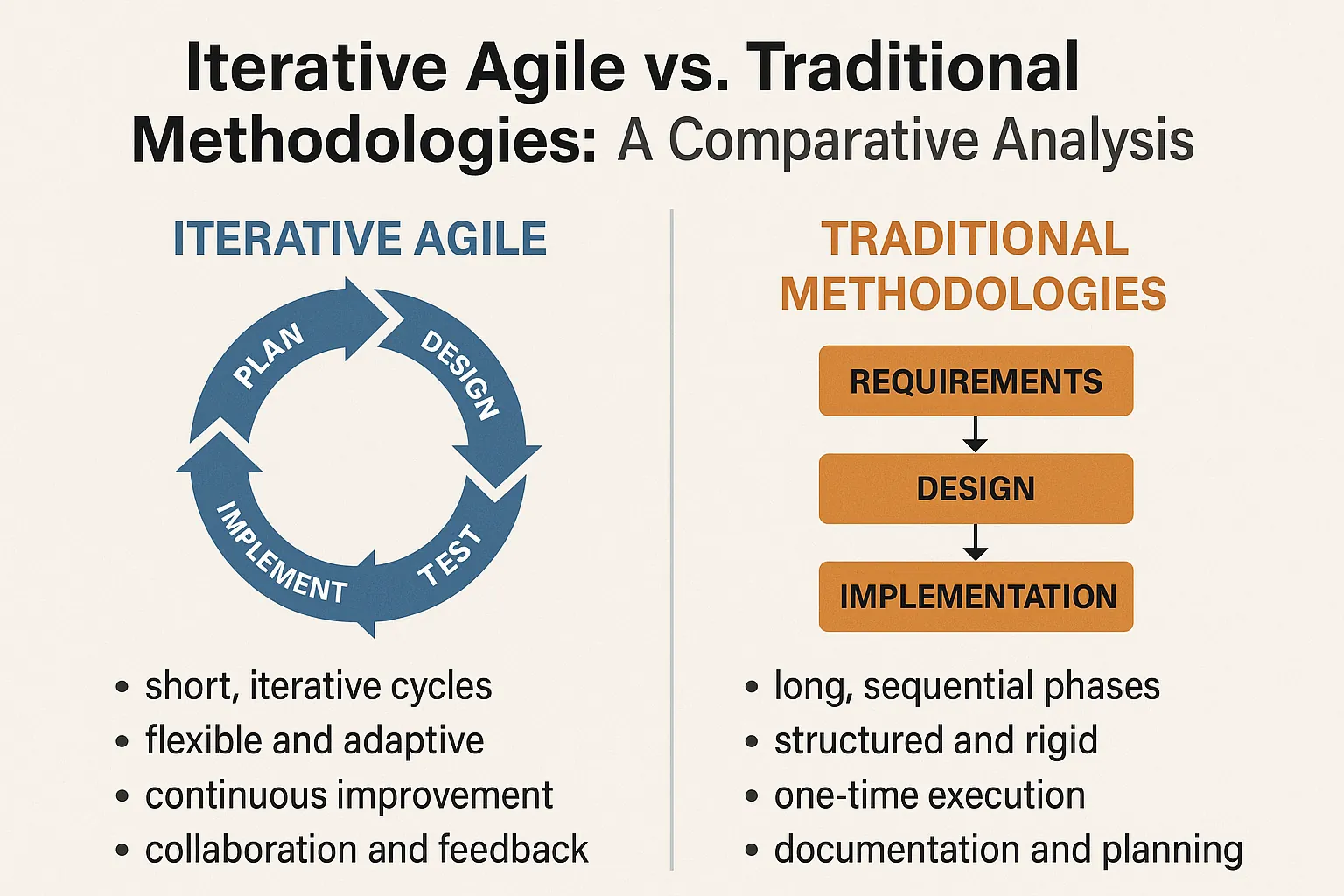
The program life cycle encompasses the series of phases that a program undergoes from initiation to closure. It typically includes the following stages:
- Initiation: This phase involves defining the program’s objectives, scope, and stakeholders. It sets the foundation for what the program aims to achieve and how it aligns with organizational goals.
- Planning: During this stage, detailed plans are developed, including resource allocation, timelines, and risk management strategies. Effective planning is critical to ensure that all aspects of the program are considered and that compliance requirements are integrated from the outset.
- Execution: This phase focuses on implementing the plans and managing the program’s activities. It requires ongoing communication and coordination among stakeholders to ensure that the program remains on track and compliant with relevant regulations.
- Monitoring and Control: Continuous oversight is essential to track progress, manage changes, and ensure adherence to compliance standards. This phase involves regular reporting and adjustments to keep the program aligned with its objectives and regulatory requirements.
- Closure: The final phase involves evaluating the program’s outcomes, documenting lessons learned, and formally closing the program. This step is vital for compliance, as it ensures that all regulatory obligations have been met and that stakeholders are informed of the results.
Overview of Program Management Concepts
Program management is a strategic approach that focuses on managing multiple related projects in a coordinated manner to achieve specific organizational objectives. Key concepts include:
- Integration: Ensuring that all projects within a program are aligned and work together towards common goals.
- Stakeholder Engagement: Actively involving stakeholders throughout the program life cycle to gather input, manage expectations, and ensure compliance with their needs and regulatory requirements.
- Risk Management: Identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks that could impact the program’s success and compliance with industry standards.
Importance of Adhering to Industry Standards and Regulations
Compliance with industry standards and regulations is not merely a legal obligation; it is a fundamental aspect of effective program management. The importance of adherence includes:
- Risk Mitigation: By following established standards, organizations can reduce the likelihood of legal issues, financial penalties, and reputational damage.
- Quality Assurance: Compliance ensures that programs meet quality benchmarks, which can enhance stakeholder trust and satisfaction.
- Operational Efficiency: Adhering to regulations can streamline processes and improve resource allocation, ultimately leading to more successful program outcomes.
Stages of the Program Life Cycle
Understanding the program life cycle is crucial for ensuring compliance with industry standards and regulations. Each stage of the program life cycle presents unique compliance requirements that must be addressed to achieve successful outcomes. Below, we break down the key stages of the program life cycle and highlight the compliance necessities at each phase.
1. Initiation: Identifying Compliance Needs and Stakeholder Expectations
The initiation phase is where the foundation for compliance is laid. During this stage, project managers and compliance officers must:
- Identify Compliance Requirements: Understand the legal, regulatory, and organizational standards that apply to the program. This includes industry-specific regulations and any relevant local, state, or federal laws.
- Engage Stakeholders: Gather input from stakeholders to ascertain their expectations regarding compliance. This engagement helps in aligning the program objectives with stakeholder needs and regulatory requirements.
- Document Compliance Needs: Create a compliance checklist that outlines all identified requirements, ensuring that they are referenced throughout the program life cycle.
2. Planning: Establishing Compliance Frameworks and Standards
In the planning stage, the focus shifts to developing a robust compliance framework that will guide the program’s execution. Key activities include:
- Developing Compliance Policies: Formulate policies that reflect the compliance requirements identified during the initiation phase. These policies should be clear, actionable, and tailored to the specific needs of the program.
- Setting Standards and Procedures: Establish standards and procedures that will govern compliance throughout the program. This includes defining roles and responsibilities for compliance management.
- Risk Assessment: Conduct a risk assessment to identify potential compliance risks and develop mitigation strategies. This proactive approach helps in minimizing compliance-related issues during execution.
3. Execution: Implementing Compliance Measures During Program Delivery
During the execution phase, compliance measures must be actively implemented to ensure adherence to established standards. This involves:
- Training and Awareness: Provide training for team members on compliance policies and procedures. Ensuring that everyone understands their responsibilities is critical for maintaining compliance.
- Integrating Compliance into Processes: Embed compliance checks into the program’s processes and workflows. This integration helps in identifying and addressing compliance issues in real-time.
- Documentation: Maintain thorough documentation of compliance activities, including any deviations from established standards and the rationale behind them.
4. Monitoring and Controlling: Tracking Compliance Adherence and Performance
The monitoring and controlling phase is essential for ensuring that compliance is maintained throughout the program. Key actions include:
- Regular Audits and Reviews: Conduct regular audits to assess compliance adherence. These reviews should evaluate whether the program is meeting its compliance objectives and identify areas for improvement.
- Performance Metrics: Establish performance metrics related to compliance. These metrics can help in tracking compliance adherence and provide insights into the program’s overall performance.
- Issue Resolution: Implement a process for addressing compliance issues as they arise. This includes documenting issues, determining their impact, and taking corrective actions.
5. Closure: Ensuring Compliance Documentation and Lessons Learned are Recorded
The closure phase is critical for finalizing compliance efforts and ensuring that lessons learned are documented for future programs. This includes:
- Final Compliance Review: Conduct a final review of compliance documentation to ensure that all requirements have been met. This review should confirm that all compliance-related activities have been properly recorded.
- Lessons Learned: Document lessons learned related to compliance throughout the program. This information can be invaluable for future projects and can help in refining compliance processes.
- Archiving Compliance Records: Ensure that all compliance documentation is archived in accordance with regulatory requirements. This archiving is essential for future audits and reviews.
By understanding and addressing compliance requirements at each stage of the program life cycle, project managers and compliance officers can ensure that their programs not only meet industry standards but also achieve their intended outcomes effectively.
The Role of Compliance in Program Management
Compliance is not merely a regulatory checkbox; it is a fundamental component that can significantly influence the success and sustainability of a program. For compliance officers and project managers, understanding the intricacies of compliance within the program life cycle is essential. Here are some key points that highlight the critical role compliance plays in program management:
Understanding Regulatory Requirements Specific to the Industry
- Industry-Specific Regulations: Each industry has its own set of regulatory requirements that govern operations, safety, and reporting. For instance, healthcare programs must comply with HIPAA regulations, while financial services must adhere to SEC guidelines. Familiarity with these regulations is crucial for program managers to ensure that all aspects of the program align with legal standards.
- Continuous Monitoring: Compliance is not a one-time effort; it requires ongoing monitoring and adaptation to changes in regulations. Program managers must stay informed about updates in laws and standards that could impact their projects, ensuring that compliance is integrated into every phase of the program life cycle.
Impact of Non-Compliance on Program Outcomes
- Financial Consequences: Non-compliance can lead to significant financial repercussions, including fines, penalties, and increased scrutiny from regulatory bodies. These financial burdens can derail a program’s budget and timeline, ultimately affecting its viability.
- Reputational Damage: Beyond financial implications, non-compliance can tarnish an organization’s reputation. Stakeholders, including clients and partners, may lose trust in an organization that fails to adhere to regulations, which can hinder future business opportunities and collaborations.
- Project Delays: Non-compliance can result in project delays as organizations may need to halt operations to address compliance issues. This not only affects the current program but can also disrupt future initiatives, leading to a cycle of inefficiency.
Benefits of Proactive Compliance Management
- Enhanced Program Success: By integrating compliance into the program management process from the outset, organizations can enhance the likelihood of program success. Proactive compliance management ensures that potential issues are identified and addressed early, reducing the risk of costly setbacks.
- Improved Stakeholder Confidence: Demonstrating a commitment to compliance can bolster stakeholder confidence. When stakeholders see that an organization prioritizes adherence to regulations, they are more likely to support the program and engage positively with the organization.
- Sustainable Practices: Proactive compliance management fosters sustainable practices within the program. By aligning with industry standards and regulations, organizations can create programs that not only meet current requirements but are also adaptable to future changes, ensuring long-term success.
Best Practices for Ensuring Compliance in Program Management
Ensuring compliance with industry standards and regulations is not just a best practice; it is a necessity. Compliance officers and project managers must work collaboratively to navigate the complexities of regulatory requirements while delivering successful programs. Here are some actionable strategies and best practices to enhance compliance in program management:
1. Developing a Compliance Checklist for Each Program Phase
Creating a comprehensive compliance checklist tailored to each phase of the program life cycle is essential. This checklist should include:
- Regulatory Requirements: Identify specific regulations applicable to the program.
- Documentation Standards: Outline necessary documentation and reporting requirements.
- Approval Processes: Define the steps for obtaining necessary approvals at each phase.
- Risk Assessment: Include criteria for assessing compliance risks associated with program activities.
By utilizing a checklist, project managers can ensure that all compliance aspects are addressed systematically, reducing the risk of oversight and enhancing accountability throughout the program life cycle.
2. Engaging Stakeholders in Compliance Discussions
Engaging stakeholders early and often in compliance discussions fosters a culture of transparency and shared responsibility. This can be achieved through:
- Regular Meetings: Schedule periodic meetings with stakeholders to discuss compliance issues and updates.
- Feedback Mechanisms: Implement channels for stakeholders to provide input on compliance processes and challenges.
- Collaborative Workshops: Organize workshops that focus on compliance training and best practices, encouraging active participation from all stakeholders.
By involving stakeholders, project managers can gain valuable insights and foster a collaborative environment that prioritizes compliance.
3. Regular Training and Updates for Team Members on Compliance Standards
Continuous education is vital for maintaining compliance. Project managers should implement regular training sessions that cover:
- Current Regulations: Update team members on any changes in industry regulations and standards.
- Compliance Procedures: Reinforce the importance of following established compliance procedures and protocols.
- Case Studies: Use real-world examples to illustrate the consequences of non-compliance and the benefits of adhering to standards.
By keeping team members informed and educated, organizations can minimize compliance risks and enhance overall program effectiveness.
4. Utilizing Compliance Management Tools and Software
Leveraging technology can significantly streamline compliance management processes. Consider the following tools and software:
- Compliance Tracking Software: Use software that allows for real-time tracking of compliance activities and documentation.
- Automated Reporting Tools: Implement tools that automate compliance reporting, reducing manual errors and saving time.
- Risk Management Platforms: Utilize platforms that help identify, assess, and mitigate compliance risks throughout the program life cycle.
By integrating compliance management tools, project managers can enhance efficiency, ensure accuracy, and maintain a proactive approach to compliance.
Challenges in Meeting Compliance Standards
Compliance with industry standards and regulations is not just a best practice; it is a necessity that ensures the integrity and success of projects. However, navigating the complexities of compliance can present several challenges. Below are some of the common obstacles faced by compliance officers and project managers, along with strategies to overcome them.
1. Complexity of Regulations and Standards
The landscape of regulations and standards is often intricate and constantly evolving. Compliance officers and project managers must stay abreast of various local, national, and international regulations that can impact their programs. This complexity can lead to:
- Misinterpretation of Requirements: Different interpretations of regulations can result in non-compliance.
- Increased Workload: Keeping up with changes requires significant time and effort, diverting focus from core project activities.
Overcoming the Challenge:
- Regular Training and Education: Implement ongoing training programs to ensure that all team members are aware of current regulations and compliance requirements.
- Utilize Compliance Management Tools: Invest in software solutions that help track regulatory changes and provide alerts for updates relevant to your projects.
2. Resource Limitations and Budget Constraints
Many organizations face limitations in resources and budget, which can hinder their ability to maintain compliance. This can manifest in several ways:
- Insufficient Staffing: A lack of dedicated compliance personnel can lead to oversight and errors.
- Limited Financial Resources: Budget constraints may prevent the acquisition of necessary tools or training programs.
Overcoming the Challenge:
- Prioritize Compliance in Budgeting: Make compliance a key component of project budgeting to ensure adequate resources are allocated.
- Leverage Cross-Functional Teams: Utilize existing staff from various departments to share the compliance workload, fostering a collaborative approach.
3. Resistance to Change Among Team Members
Implementing compliance measures often requires changes in processes and workflows, which can meet resistance from team members. Common issues include:
- Fear of Increased Workload: Team members may perceive compliance initiatives as adding to their responsibilities.
- Cultural Resistance: Established practices may be deeply ingrained, making it difficult to introduce new compliance protocols.
Overcoming the Challenge:
- Engage Stakeholders Early: Involve team members in the compliance planning process to foster buy-in and reduce resistance.
- Communicate the Benefits: Clearly articulate how compliance measures can enhance project success and protect the organization, thereby motivating team members to embrace change.
4. Strategies for Effective Change Management
To successfully implement compliance measures, effective change management strategies are essential. These strategies can help mitigate the challenges outlined above:
- Develop a Change Management Plan: Create a structured approach that outlines the steps for implementing compliance changes, including timelines and responsibilities.
- Monitor and Evaluate: Regularly assess the effectiveness of compliance initiatives and make adjustments as necessary to ensure ongoing adherence to standards.
By addressing these challenges head-on, compliance officers and project managers can enhance their program management practices, ensuring that compliance is not just an obligation but a pathway to project success.
Conclusion: The Future of Compliance in Program Life Cycle
The importance of compliance remains a critical focus for organizations striving to meet industry standards and regulations. The following key points highlight the ongoing necessity of compliance in the program life cycle:
- Evolving Nature of Regulations and Standards: Regulatory frameworks and industry standards are not static; they are continually updated to reflect new challenges, technologies, and societal expectations. Compliance officers and project managers must stay informed about these changes to ensure that their programs align with current requirements. This adaptability is essential for mitigating risks and maintaining organizational integrity in a dynamic environment.
- Role of Technology in Enhancing Compliance: Technology plays a pivotal role in streamlining compliance processes. Advanced tools such as compliance management software, data analytics, and automated reporting systems can significantly enhance an organization’s ability to monitor adherence to regulations. By leveraging these technologies, compliance officers can improve efficiency, reduce human error, and ensure that compliance measures are integrated throughout the program life cycle.
- Encouragement for a Culture of Compliance: Fostering a culture of compliance within organizations is crucial for long-term success. This involves not only adhering to regulations but also promoting ethical practices and accountability at all levels. Training and awareness programs can empower employees to understand the importance of compliance, encouraging them to take ownership of their roles in maintaining standards. A strong compliance culture not only protects the organization but also enhances its reputation and stakeholder trust.
In conclusion, as program management continues to adapt to new challenges and opportunities, the emphasis on compliance will only grow stronger. By understanding the evolving nature of regulations, embracing technological advancements, and cultivating a culture of compliance, organizations can navigate the complexities of the program life cycle effectively. This proactive approach will not only ensure compliance but also drive organizational success in an increasingly regulated world.
Find out more about Shaun Stoltz https://www.shaunstoltz.com/about/.
This post was written by an AI and reviewed/edited by a human.